Ataxia is an affection that causes the lack of coordination in a patient. People who suffer from any type of ataxia are not able to control their muscles, they encounter issues with stability and they even face problems when they have to walk. Ataxia can affect the whole body or only parts of it such as the fingers, hands, arms, or feet. Sometimes, ataxia can affect the movement of the eyes or even the patient’s speech. Usually, ataxia is a symptom of diseases or degenerative changes in the central nervous system, but it can become a disease on its own. There are two types of ataxia that are considered diseases: hereditary and sporadic. When no other cases of ataxia are present in a family’s medical history, but a member suffers from ataxia, the disease is called sporadic; otherwise, it is hereditary. Sporadic ataxia occurs only in adulthood, while hereditary ataxia can appear early in childhood.
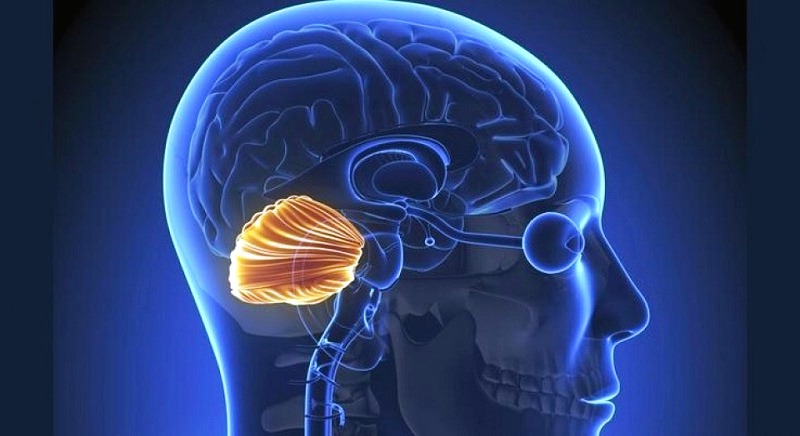
The cause of ataxia is represented by cerebral cell atrophy. The part of the brain responsible for coordinating muscle movements and maintaining posture/balance is called the cerebellum and it is located in the back of the head. Any trauma or degeneration to this area can lead to ataxia. It can also be triggered by abnormal genes that produce proteins which affect the nerve cells in the cerebellum. These proteins can affect other parts of the nervous system as well. The nerve cells that were damaged in the process will start functioning incorrectly. As a result, the muscles of the patient become unreceptive to the brain’s orders, so the person can no longer coordinate his or her movements.
Both sporadic and hereditary ataxia cause the following symptoms in a patient:
- The lack of coordination
- Unclear speech
- Encountering issues when walking
- Difficulty eating
- Impossibility to write
- Slow eye movement
Other medical conditions can also cause the aforementioned symptoms. This is the reason why it is highly important to consult a physician for a clear diagnosis. The physical examinations and screenings required for determining if a patient is suffering from ataxia include:
- Blood tests
- X-rays (internal tissues, bones)
- MRI tests
- Genetic tests (for chromosomal abnormalities)
The sudden apparition of ataxia can be triggered by trauma to the head, stroke, brain tumors, congenital abnormalities, infectious diseases, cardio-respiratory disorders and so on. The onset of ataxia can be rushed by hypothyroidism, vitamin deficiencies, certain medications, sclerosis, syphilis etc. Currently, there is no existent cure for hereditary ataxia, although researchers are trying their best to find an appropriate solution for the problem. There are no drugs able to treat the symptoms generated by hereditary ataxia. The only measurement patients can take is adapting the environment they are surrounded by to the lack of coordination and stability they struggle with every day. The goal is to maintain the independence of a person for as long as possible. Medical devices such as walking aids and wheelchairs can be helpful, while physical therapy and speech therapy can improve a part of the symptoms.